WHAT IS GEOELECTRIC?
Geoelectrics is a branch of Geophysics that examines how rocks and sediments react to an electric current transmitted through the ground. The primary physical parameter measured is resistivity, and the final interpretation is based on the geological characteristics of the area where geoelectric prospecting methods are employed.


HOW DOES GEOELECTRICITY WORK?
Geoelectrics involves injecting an electric current into the subsurface using an array of electrodes. This current generates a potential difference, which is measured by specialized instruments and then translated into resistivity values.
WHY GEOELECTRIC?
- It provides high-resolution imaging of subsurface features.
- It is a non-invasive method that does not disturb the ground.
- It allows for accurate determination of the depth and size of subsurface features.
- The data is stored on a hard disk for later analysis and processing.
- It offers detailed information about physical properties, particularly in areas that are challenging to sample directly.

INDUSTRIES AND APPLICATIONS THAT MOST USE GEOELECTRICITY
- Conduct a search on groundwater
- Evaluation of the depth of the bedrock substrate
- Identification of contamination sources
- Identification of fractures and geological faults
- Topography of landfills
- Geological assessment for tunnel construction
- Mining exploration and landslide movement analysis
- Topographic mapping of natural or artificial (subway) tunnels
- Mining cavities
GEOELECTRICAL CONFIGURATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
IP
SP
Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES)
Electrical Tomography
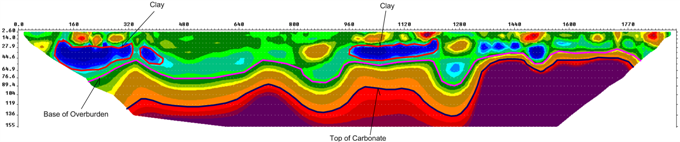
RESULTS AND PROCESSING
2D Inversion
2.5D Inversion
3D Inversion
Pseudosections